What is Vacuum Casting?
Introduction
Vacuum Casting is a copying method used to mold thermosetting polyurethane (PU) for fast production of prototypes or end-use products. There are many different types of PU, which makes this process suitable for the majority of plastic prototyping. It is sometimes also known as Urethane Casting/Polyurethane Casting or Silicone Mold Casting.
Vacuum Casting is used to simulate the materials and the processing capabilities of injection molding. It can replicate almost all the properties of injection molding. Vacuum Casting is very suitable for one-off and low volume of production due to its advantage of low tooling cost and quicker production time in comparison to injection molding. It is used for a diversity of prototyping applications including automotive components, sports equipment and medical instruments.
Applications
- Proof-of-Concept Model
- Visual prototypes
- Low volume production
- Product testing

Vacuum Casting Process
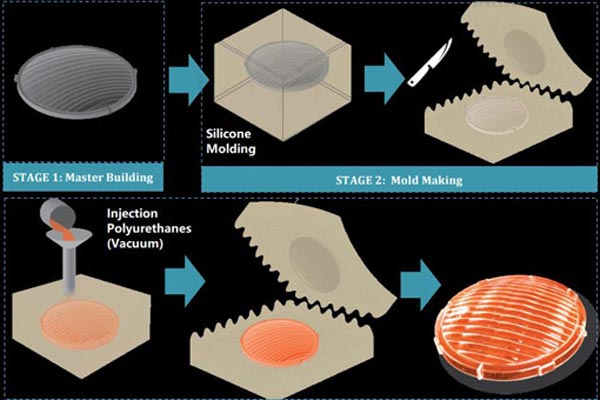
STAGE 1: Master Building
Master patterns are 3D solid parts of your CAD designs. They can be done via CNC machining or by 3D printing (usually SLA). The master patterns will then be surface finished and inspected before moving to the next step of mold making.
STAGE 2: Mold Making
Casting molds are made from liquid silicone. The master pattern is suspended in a box by the gate, runners and riser. The box is then filled with silicone rubber, which completely encapsulates it.
When the silicone mold is fully cured, the mold is separated into halves by cutting into the silicone mold to meet the pattern. This is a very skillful process and the part geometry will determine the mold making technique. The master pattern is then removed from the mold.
STAGE 3: Part Making
The casting process takes place under vacuum. The polyurethane resin pours into the mold cavity to create a highly accurate copy of the original. It’s even possible to over-mold with two or more materials. The mold is left in an oven at 40°C until the PU has fully cured.
The final casted part will then be released from the mold by detaching the two halves of the silicone mold.
Compatible Materials
PU is a 2-part thermosetting plastic. When 2 parts are mixed in the right positions, the polymerization process will take place.
There are several hundred different grades of PU in the market that can mimic the performance of plastic injection molding such as PP-like, ABS-like, PMMA-like, PC-like and rubber-like materials. These materials provide an outstanding variety of properties and offer different possibility to match colors. Besides that, additives can be added to improve flame retardant qualities, heat resistance and UV stability.
Why Choose Vacuum Casting?
1. Superior Surface Finish and A Variety of Finishing Degrees
The vacuum casting process is taking place under a vacuum environment. It allows the material to capture fine details of the master pattern and the surface finish will be an exact replica of the pattern. Hence, vacuum casting offers a superior surface finish and a variety of surface textures for the casted parts.
2. Variety of Colors
Color pigments can be added to the PU for a variety of color options.
3. Fast Turnaround
Vacuum casting offer quality parts in shorter lead-time than traditional tooling and molding. Fast cycle time (typically hours to several days) depending on the volume, size and complexity of the part.
4. Affordability
Silicone molds are generally low and less expensive than the steel tool used for plastic injection molding. Labor costs are moderate. Mold making, vacuum casting and finishing are all carried out manually.
5. Repeatability
Silicone mold can be utilized up to 20 times before it degrades. For high gloss part, it might need to be replaced after 15 times, dependent on the complexity of the part.
